


TIMELY INTERVENTION IS CRITICAL
Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2 has been linked to mortality in COVID-19.
1
GM-CSF is an early initiator of the cytokine response.
Many deaths are attributed to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multiorgan failure that arises from an immune hyper-response, or cytokine storm.
1,2
The Patient Journey With COVID-19 Cytokine Storm
3-5
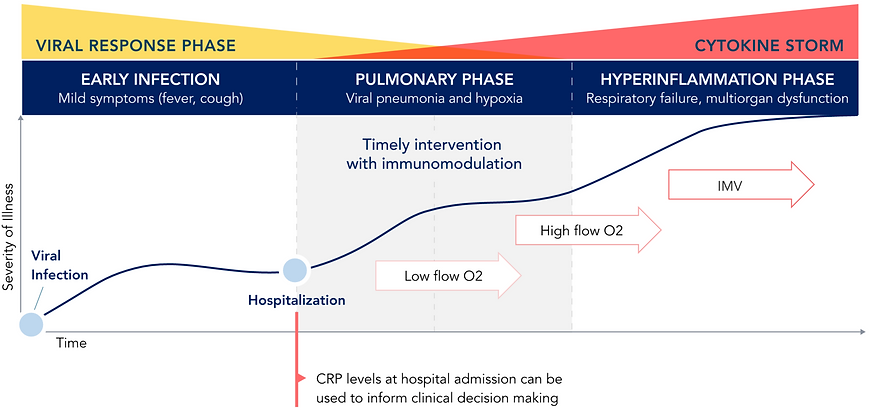
COVID-19 disease progression can be divided into 3 stages: early infection, pulmonary phase, and hyperinflammation phase. Most patients in the pulmonary stage have moderate disease and require hospitalization, and levels of CRP can inform clinical decision-making. As patients progress to the hyperinflammation stage, their oxygen requirement increases.
3
3,5
3
Once patients need ventilatory support, their disease could be at an accelerated state where the interventions may be less effective or futile.
6
Targeting cytokines such as GM-CSF through immunomodulation could serve as an important option for hospitalized patients who are experiencing hypoxia but are not on invasive mechanical ventilation.
6
Timely and early intervention in the cytokine storm cascade has the potential to prevent progression to mechanical ventilation and mortality associated with COVID-19
6

For US Healthcare Professionals Only
References:
1.
Ragab D, Salah Eldin H, Taeimah M, Khattab R, Salem R. The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1446.
2.
Moore JB, June CH. Cytokine release syndrome in severe COVID-19. Science. 2020;368(6490):473-474.
3.
Siddiqi HK, Mehra MR. COVID-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2020;39(5):405-407.
4.
WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection. A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(8):e192-e197.
5.
Manson JJ, Crooks C, Naja M, et al. COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: a retrospective longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020;2(10):e594-e602.
6.
Mehta P, Porter JC, Manson JJ, et al. Therapeutic blockade of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation: challenges and opportunities. Lancet Respir Med. 2020;8(8):822-830.